Discover the hidden science behind your favorite cup of tea! This post takes you on a deep dive into the nootropic ingredients in tea—focusing on how compounds like caffeine, L-theanine, polyphenols, EGCG, and theaflavins work together to boost your brain power. Unlike our broader ultimate guide on cognitive teas, this article zooms in on research-backed details, clinical evidence, and practical tips for optimizing your brew to extract maximum cognitive benefits. Perfect for health enthusiasts, working professionals, researchers, and anyone curious about natural nootropics.
Introduction: Focusing on the Science of Tea’s Nootropic Power
While many appreciate tea for its soothing flavor and cultural significance, there’s a powerful, scientific story hidden in every cup. This post is not your general overview of cognitive teas—it’s a dedicated exploration of the specific nootropic ingredients in tea and the research that confirms their brain-boosting benefits. We peel back the layers and examine how each component, from caffeine to the unique antioxidants like EGCG, contributes to enhanced focus, memory, and overall cognitive performance.
This deep dive covers the science behind tea’s nootropic properties. It’s all about understanding the molecular magic: how caffeine provides a gentle stimulation, how L-theanine creates a calm alertness, and how polyphenols and theaflavins offer robust antioxidant protection. In essence, this post is designed for those who crave a data-driven, research-backed perspective on how natural nootropics in tea can power up your brain.
The Science of Nootropic Compounds in Tea
Tea contains a complex of bioactive compounds that work together to support cognitive health. Let’s break down these key players and uncover how each contributes to your brain’s performance.
Caffeine & L-Theanine: The Synergistic Duo
Caffeine and L-theanine, both found in tea, work together to enhance cognitive performance and mood, creating a state of “calm alertness.” This combination is particularly effective in improving attention and reducing the overstimulation often associated with caffeine or coffee alone.

Effects of Caffeine and L-Theanine
- Cognitive Performance: The combination of caffeine and L-theanine improves cognitive performance, particularly in tasks requiring attention switching and sustained attention. This synergy enhances accuracy and reduces error rates in cognitive tasks, suggesting a beneficial interaction between the two compounds.1 2 3 4
- Mood and Alertness: Caffeine increases alertness and reduces mental fatigue, while L-theanine contributes to a calming effect, smoothing out the stimulating effects of caffeine. This results in increased subjective alertness without the jitteriness often associated with caffeine alone.2 3 5 6
- Physiological Effects: L-theanine can counteract some of the physiological effects of caffeine, such as increased blood pressure, without significantly affecting alertness or mood. This interaction may explain why tea is perceived as less stimulating than coffee.67
Mechanisms of Action
- Neurochemical Interaction: L-theanine modulates brain function by increasing alpha-band activity, which is associated with relaxation without drowsiness. This effect complements caffeine’s ability to enhance alertness and cognitive performance.1 8
- Task Performance: The combination of caffeine and L-theanine is particularly effective in improving performance on tasks that require sustained attention and rapid information processing, highlighting their complementary roles in enhancing cognitive function.2 4 9
The combination of caffeine and L-theanine in tea provides a balanced enhancement of cognitive performance and mood, promoting a state of calm alertness. This synergy allows for improved attention and reduced fatigue without the negative side effects often associated with caffeine alone.
Polyphenols and EGCG: The Antioxidant Arsenal
Beyond its stimulating effects, tea is loaded with polyphenols—powerful antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress, a major factor in cognitive decline. Among these, Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) stands out for its remarkable neuroprotective properties.
- Polyphenols:
- Help neutralize free radicals, protecting brain cells from damage.
- Supports overall cardiovascular and brain health by reducing inflammation.
- EGCG:
- Provides potent antioxidant protection, which has been linked to improved memory and learning abilities.
- Is recognized for their neuroprotective properties, primarily due to their antioxidant capabilities. These compounds help combat oxidative stress, a significant factor in cognitive decline.
Neuroprotective Mechanisms
- Antioxidant Activity: Tea polyphenols, including EGCG, exhibit strong antioxidant properties that mitigate oxidative stress-induced cellular damage, which is a major contributor to cognitive impairment.10 11 12
- Signaling Pathways: They activate pathways such as TrkB/CREB/BDNF and Keap1/Nrf2, which are crucial for neuroprotection and cognitive function.10 13
- Inflammation Reduction: Green tea catechins and other polyphenols reduce neuroinflammation, which is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.14 15
Cognitive Benefits
- Improvement in Cognitive Function: Studies have shown that tea polyphenols can enhance cognitive functions such as memory, language, and subjective cognitive ability, particularly in individuals with early cognitive decline.16 17
- Neuroprotection in Aging: Regular consumption of green tea polyphenols has been associated with improved cognitive performance in aging populations, potentially delaying the onset of neurodegenerative diseases.11 18
Tea polyphenols, especially EGCG, offer significant neuroprotective benefits by combating oxidative stress and inflammation, enhancing cognitive function, and potentially delaying neurodegenerative processes. While more human studies are needed, the current evidence supports their role as a promising non-pharmacological intervention for cognitive decline.
Additional Compounds: The Role of Theaflavins and Beyond
In addition to the well-known compounds, tea also contains theaflavins—especially prominent in black tea—which contribute to its overall cognitive benefits. Theaflavins enhance the antioxidant profile of tea and support gut health, an emerging factor in maintaining optimal brain function.
Cognitive Benefits of Theaflavins
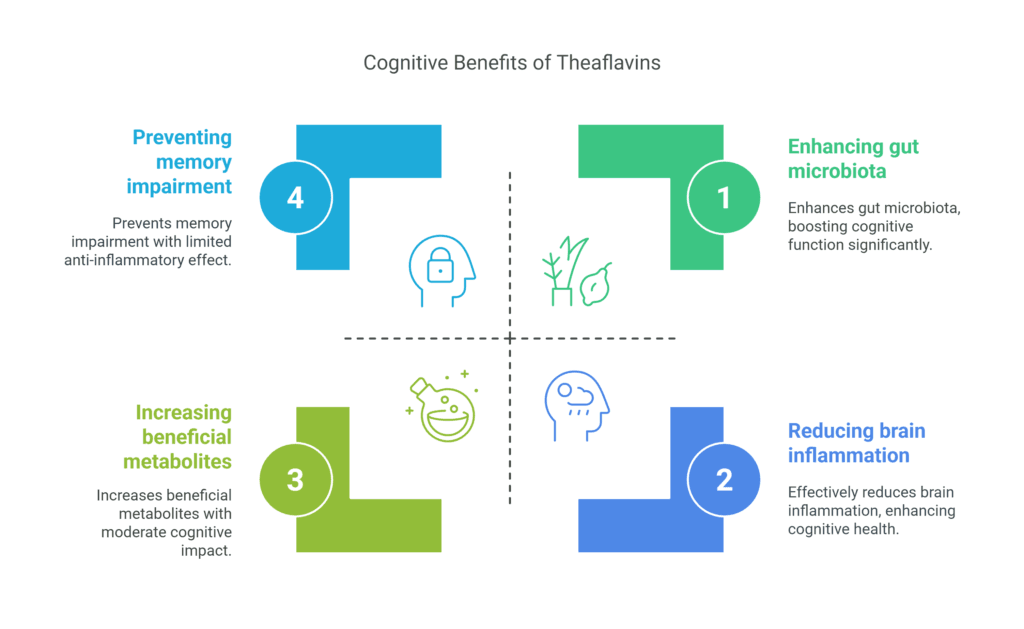
- Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Theaflavins improve cognitive function by maintaining gut homeostasis, enhancing antioxidant capacity, and modulating gut microbiota. This includes increasing beneficial metabolites like short-chain fatty acids and amino acids, which are linked to improved brain health and behavior.19
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Theaflavins exhibit strong anti-inflammatory properties, surpassing other polyphenols like catechins. They reduce brain inflammation, protect synapses, and prevent memory impairment and depression-like behaviors in animal models.20
Antioxidant Properties
- Superior Antioxidant Capacity: Theaflavins have a higher antioxidant potential compared to other tea polyphenols, such as epigallocatechin gallate. This is due to their unique chemical structure, which enhances their ability to neutralize oxidative stress.21 22
- Neuroprotective Effects: Theaflavins demonstrate significant neuroprotective effects by improving sensorimotor function and reducing oxidative stress markers in animal studies, suggesting their potential in mitigating neurodegenerative conditions.22
Theaflavins in black tea offer significant cognitive benefits through their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They support gut health, which is increasingly recognized as vital for brain function, and provide a promising dietary intervention for cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Optimizing Your Brew for Maximum Cognitive Benefits
Unlocking the full power of tea’s nootropic ingredients isn’t just about choosing the right tea—it’s also about perfecting your brewing technique. Here are some science-based tips to ensure you’re extracting every bit of cognitive benefit:
Best Practices for Brewing
- Temperature Control:
- Green Tea: Heat water to approximately 175°F (80°C) to preserve delicate compounds like L-theanine and polyphenols.
- Black Tea: Use water around 200°F (93°C) to effectively extract robust flavors and theaflavins.
- Precise Steeping Time:
- Aim for 2–3 minutes for green tea and 4–5 minutes for black tea. Over-steeping may cause bitterness and reduce the effectiveness of the compounds.
- Water Quality:
- Always opt for filtered or spring water. Hard tap water can contain minerals that interfere with the extraction process and alter flavor.

Daily Integration Strategies
For those serious about leveraging tea as a natural nootropic:
- Morning Routine: Start with a cup of green tea or matcha to gently stimulate your brain without overwhelming it.
- Mid-Day Refresh: If your focus begins to wane, switch to a cup of peppermint or yerba mate tea for a quick cognitive lift.
- Mindful Brewing Rituals: Treat your tea preparation as a mini science experiment—measure precisely, use the right temperature, and time your steeping accurately.
Following these guidelines will ensure that every cup of tea you prepare is optimized to deliver the full spectrum of cognitive benefits, allowing you to truly harness the power of natural nootropics.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tea Nootropics
Wrapping Up: Elevate Your Brain Power One Cup at a Time
Tea is more than just a comforting ritual—it’s a scientifically validated natural nootropic that can elevate your cognitive function with every carefully brewed cup. By delving into the science behind its key ingredients, such as caffeine, L-theanine, polyphenols, EGCG, and theaflavins, we’ve uncovered how these compounds interact to promote calm alertness and protect your brain from the stresses of daily life.
This deep-dive into tea’s nootropic properties is designed for those who crave a research-backed perspective on natural cognitive enhancement. Remember, optimizing your brewing technique is just as important as choosing the right tea. From precise temperature control to mindful steeping practices, every detail matters when you’re tapping into nature’s brain boosters.
Ready to boost your brain health naturally?
Subscribe to our newsletter for updates on new blog posts, news, reviews, and guides.
Join Our Newsletter
Receive updates on new blog posts, news, reviews, and guides
Additional Resources and Final Thoughts
For those who wish to dive deeper:
- Explore More: Read our comprehensive Comparative Review of Cognitive Teas vs. Traditional Teas.
- Internal Links: Visit our posts on Brewing Techniques & DIY Tea Recipes and Ultimate Guide to Cognitive Teas for further insights.
In a world where every sip matters, choosing the right tea isn’t just about flavor—it’s about enhancing your overall well-being. Whether you lean towards the innovative edge of cognitive teas or the enduring tradition of classic teas, your perfect cup awaits. Cheers to a brighter, more focused you!
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for any health concerns.
Sources
- Bryan, J. (2008). Psychological effects of dietary components of tea: caffeine and L-theanine.. Nutrition reviews, 66 2, 82-90 . https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.00011.x.
- Haskell, C., Kennedy, D., Milne, A., Wesnes, K., & Scholey, A. (2008). The effects of l-theanine, caffeine and their combination on cognition and mood. Biological Psychology, 77, 113-122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2007.09.008.
- Giesbrecht, T., Rycroft, J., Rowson, M., & Bruin, E. (2010). The combination of L-theanine and caffeine improves cognitive performance and increases subjective alertness. Nutritional Neuroscience, 13, 283 – 290. https://doi.org/10.1179/147683010X12611460764840.
- Foxe, J., Morie, K., Laud, P., Rowson, M., Bruin, E., & Kelly, S. (2012). Assessing the effects of caffeine and theanine on the maintenance of vigilance during a sustained attention task. Neuropharmacology, 62, 2320-2327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.01.020.
- Camfield, D., Stough, C., Farrimond, J., & Scholey, A. (2014). Acute effects of tea constituents L-theanine, caffeine, and epigallocatechin gallate on cognitive function and mood: a systematic review and meta-analysis.. Nutrition reviews, 72 8, 507-22 . https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12120.
- Rogers, P., Smith, J., Heatherley, S., & Pleydell-Pearce, C. (2007). Time for tea: mood, blood pressure and cognitive performance effects of caffeine and theanine administered alone and together. Psychopharmacology, 195, 569-577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0938-1.
- Dodd, F., Kennedy, D., Riby, L., & Haskell-Ramsay, C. (2015). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effects of caffeine and L-theanine both alone and in combination on cerebral blood flow, cognition and mood. Psychopharmacology, 232, 2563 – 2576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3895-0.
- Nobre, A., Rao, A., & Owen, G. (2008). L-theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state.. Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition, 17 Suppl 1, 167-8 . https://doi.org/10.6133/APJCN.2008.17.S1.40.
- Einöther, S., Martens, V., Rycroft, J., & Bruin, E. (2010). l-Theanine and caffeine improve task switching but not intersensory attention or subjective alertness. Appetite, 54, 406-409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2010.01.003.
- Qi, G., Mi, Y., Wang, Y., Li, R., Huang, S., Li, X., & Liu, X. (2017). Neuroprotective action of tea polyphenols on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of the TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in SH-SY5Y cells and mice brain.. Food & function, 8 12, 4421-4432 . https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fo00991g.
- Weinreb, O., Mandel, S., Amit, T., & Youdim, M. (2004). Neurological mechanisms of green tea polyphenols in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 15 9, 506-16 . https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNUTBIO.2004.05.002.
- Shaukat, H., Ali, A., Zhang, Y., Ahmad, A., Riaz, S., Khan, A., Mehany, T., & Qin, H. (2023). Tea polyphenols: extraction techniques and its potency as a nutraceutical. , 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2023.1175893.
- Song, Y., Li, X., Gong, X., Zhao, X., , Z., Xia, T., & Gu, X. (2019). Green tea polyphenols improve isoflurane-induced cognitive impairment via modulating oxidative stress.. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 73, 108213 . https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNUTBIO.2019.07.004.
- Farzaei, M., Bahramsoltani, R., Abbasabadi, Z., Braidy, N., & Nabavi, S. (2018). Role of green tea catechins in prevention of age‐related cognitive decline: Pharmacological targets and clinical perspective. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234, 2447 – 2459. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27289.
- Song, Z., Ho, C., & Zhang, X. (2024). Gut Microbiota Mediate the Neuroprotective Effect of Oolong Tea Polyphenols in Cognitive Impairment Induced by Circadian Rhythm Disorder.. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01922.
- Ni, L., Zhao, M., Hu, Z., Yang, K., Zhao, X., Niu, H., & Lin, H. (2021). Neural Mechanism of Shentai Tea Polyphenols on Cognitive Improvements for Individuals with Subjective Cognitive Decline: A Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study.. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-210469.
- Baba, Y., Inagaki, S., Nakagawa, S., Kaneko, T., Kobayashi, M., & Takihara, T. (2020). Effect of Daily Intake of Green Tea Catechins on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Subjects: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Molecules, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184265.
- Xu, Y., Zhang, J., Xiong, L., Zhang, L., Sun, D., & Liu, H. (2010). Green tea polyphenols inhibit cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via modulating oxidative stress.. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 21 8, 741-8 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.05.002.
- Li, M., Zhang, C., Xiao, X., Zhu, M., Quan, W., Liu, X., Zhang, S., & Liu, Z. (2023). Theaflavins in Black Tea Mitigate Aging-Associated Cognitive Dysfunction via the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis.. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06679.
- Ano, Y., Ohya, R., Kita, M., Taniguchi, Y., & Kondo, K. (2019). Theaflavins Improve Memory Impairment and Depression-Like Behavior by Regulating Microglial Activation. Molecules, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030467.
- Sharma, N., Phan, H., Chikae, M., Takamura, Y., Azo-Oussou, A., & Vestergaard, M. (2020). Black tea polyphenol theaflavin as promising antioxidant and potential copper chelator.. Journal of the science of food and agriculture. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10347.
- Ahmad, A., Nosheen, F., Arshad, M., Saeed, F., Afzaal, M., Islam, F., Imran, A., Noreen, R., Ali, Y., & Shah, M. (2023). Isolation and antioxidant characterization of theaflavin for neuroprotective effect in mice model. Food Science & Nutrition, 11, 3485 – 3496. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.3337.