In today’s high-pressure work environment, the right cognitive tea can provide professionals with a crucial mental edge. This comprehensive guide helps you evaluate cognitive tea products and brewing accessories based on four key criteria: targeted cognitive effects, practical workplace integration, quality indicators, and compound profiles. You’ll discover how to build a personalized tea system that addresses specific professional challenges—from sustained focus to stress resilience—and how to implement it within office constraints. Whether you’re new to cognitive teas or looking to optimize your existing routine, this evidence-based framework will help you make informed decisions that enhance your workplace performance without the jitters or crashes associated with coffee.
Introduction to Cognitive Tea Products for Professionals
The Modern Professional’s Cognitive Challenges
Today’s professionals face unprecedented cognitive demands. You’re expected to maintain laser focus during back-to-back meetings, rapidly switch between complex tasks, and make critical decisions under intense pressure—all while managing a constant stream of digital distractions.
Research from the American Institute of Stress indicates that 83% of US workers suffer from work-related stress, with 54% reporting that stress impacts their cognitive performance[1]. The resulting mental fatigue doesn’t just feel uncomfortable—it directly impacts your productivity, decision-making quality, and career trajectory.
Modern professionals are increasingly seeking effective alternatives to the traditional coffee-and-energy-drink approach, which often leads to jitters, crashes, and disrupted sleep—further compounding cognitive challenges rather than resolving them.

How Cognitive Teas Support Workplace Performance
Cognitive teas offer a sophisticated alternative to conventional stimulants by providing balanced support for brain function through a complex of bioactive compounds:
- L-theanine (prominently found in green tea) promotes alpha brain wave activity—the same pattern observed during states of “relaxed alertness”—allowing you to remain calm yet mentally sharp during high-pressure situations[2].
- Caffeine, when combined with L-theanine, provides cleaner stimulation without the jitters and anxiety commonly associated with coffee. This synergistic relationship has been shown to improve attention switching and reduce task-induced fatigue[3].
- Adaptogenic herbs like rhodiola and ashwagandha help regulate your stress response systems, enabling better resilience during challenging work periods and faster recovery afterward[4].
- Antioxidant compounds such as EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) provide neuroprotective benefits, supporting long-term brain health despite workplace stressors[5].
These natural compounds create what Dr. Andrew Huberman, neuroscientist at Stanford University, calls “a neurochemical profile conducive to sustained cognitive performance” without the rollercoaster effects of pure stimulants[6].
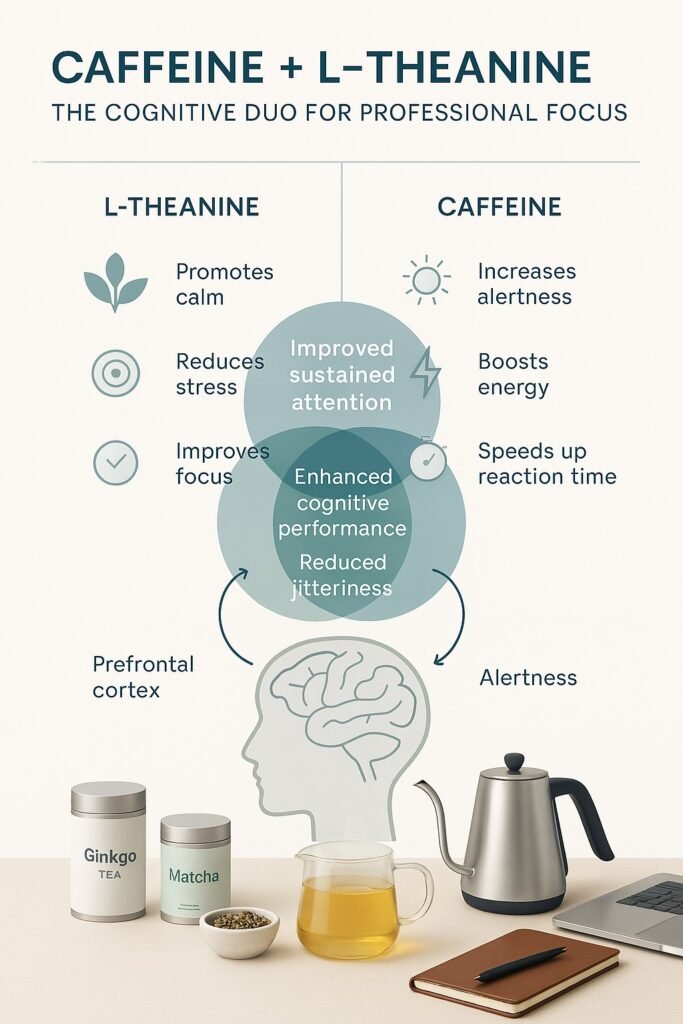
Comprehensive Evaluation Framework for Cognitive Teas
Key Assessment Criteria for Professional Use
When evaluating cognitive teas, look beyond marketing claims and consider these essential factors:
1. Targeted Cognitive Effect
Different work scenarios demand different cognitive states. Consider what aspects of performance you need to enhance:
- Deep focus work: Teas with higher L-theanine to caffeine ratios promote sustained concentration without overstimulation.
- Creative thinking sessions: Formulations with moderate caffeine and adaptogenic herbs like holy basil support relaxed-yet-alert states conducive to innovative thinking.
- High-pressure meetings: Blends with rhodiola, ginseng, or ashwagandha can help maintain mental clarity while moderating stress responses.
- Recovery periods: Caffeine-free options with adaptogenic compounds support cognitive recovery after intense work.
2. Practical Workplace Integration
The best cognitive tea is one you’ll actually use consistently:
- Preparation complexity: Consider your workplace limitations and available time for preparation. This may not be much of an issue if you are working from home.
- Equipment needs: Assess what brewing equipment is practical in your office or home office environment.
- Discreteness factor: In some professional settings, elaborate tea preparation may draw unwanted attention or create misconceptions.
3. Quality Indicators
Tea quality significantly impacts cognitive benefits:
- Tea grade: Higher grades generally contain more bioactive compounds.
- Processing methods: Less oxidized teas (white, green) preserve more L-theanine, while more oxidized varieties (black, certain oolongs) offer different antioxidant profiles.
- Freshness: Compounds degrade over time, affecting potency.
4. Compound Profile
For meaningful cognitive benefits, look for:
- L-theanine content: Quality products should contain at least 25-50mg per serving[7].
- Adaptogen standardization: Look for standardized levels of active compounds rather than simply “containing” an herb.
- Synergistic formulations: The most effective products combine compounds that work together—caffeine with L-theanine, or multiple complementary adaptogens.
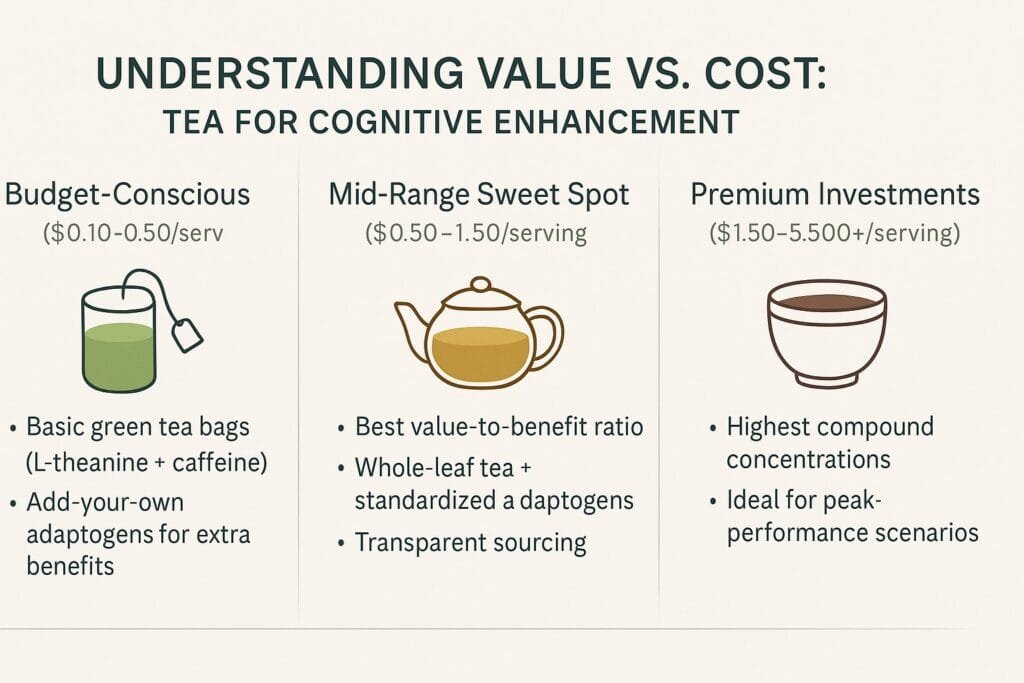
Understanding Value vs. Cost
Tea pricing varies dramatically, from $0.10 to $5+ per serving. Here’s how to evaluate true value for cognitive enhancement:
Budget-Conscious Options ($0.10-$0.50 per serving):
- Basic green tea bags from reputable brands provide baseline L-theanine and caffeine benefits.
- Some adaptogens can be purchased separately and added to basic teas for enhanced effects.
Mid-Range Sweet Spot ($0.50-$1.50 per serving):
- This range typically offers the best value-to-benefit ratio for cognitive enhancement.
- Look for whole-leaf teas with transparent sourcing and standardized adaptogenic additions.
Premium Investments ($1.50-$5.00+ per serving):
- Ceremonial grade matcha and premium adaptogenic blends offer highest compound concentrations.
- Reserve these for high-stakes professional scenarios where peak performance justifies the investment.
Value Optimization Strategies:
- Multiple infusions: Quality whole-leaf teas can be steeped multiple times, reducing per-serving cost.
- Strategic consumption: Use premium products selectively for high-value work situations.
- DIY enhancement: Purchase high-quality base tea and add separate adaptogenic tinctures or powders to create custom blends.
Essential Equipment Selection Guide
Office-Compatible Brewing Solutions
The right equipment transforms tea from an occasional indulgence to a seamless part of your professional toolkit. These solutions address common office constraints:

1. All-in-One Systems
- Self-contained brewing vessels eliminate the need for separate teapots and strainers
- Look for designs that allow you to brew and drink from the same container
- Prioritize business-appropriate aesthetics over traditional tea aesthetics
2. Temperature Management Solutions
- Accurate temperature is critical for proper extraction of cognitive compounds
- Options range from simple desk thermometers to programmable electric kettles
- For shared spaces, consider compact kettles with preset temperature buttons
3. Storage Solutions
- Proper storage preserves the potency of cognitive compounds
- Seek airtight, opaque containers that protect from light, air, and moisture
- Consider desk drawer organizers specifically designed for tea storage
Time-Optimization Equipment
When every minute counts, these tools help you integrate quality tea into even the most demanding schedules:
1. Rapid-Extraction Infusers
- Precision-engineered mesh sizes optimize extraction speed
- Look for designs that can be quickly removed and cleaned
- Some models include coloration indicators to show optimal extraction
2. Pre-Measuring Systems
- Single-serve containers eliminate measuring time
- Pre-portioned filters allow quick preparation
- Some systems include adjustable scoops calibrated to different tea types
3. Travel-Ready Solutions
- Leak-proof infuser bottles maintain quality while mobile
- Dual-chamber designs keep leaves separate until brewing
- Look for insulated options that maintain temperature for hours
Equipment Investment Strategy
Rather than purchasing everything at once, build your equipment collection strategically:
Essential Starter Kit:
- A quality infuser mug or bottle ($20-35)
- A basic temperature guide or thermometer ($5-15)
- Airtight storage containers ($10-20)
Worthwhile Upgrades:
- Temperature-controlled kettle ($40-80)
- Higher-precision infuser with optimal mesh size ($15-30)
- Travel infuser bottle for maintaining routines while mobile ($25-40)
Luxury Investments (if justified by professional needs):
- Automated brewing systems that ensure perfect extraction ($100-200)
- Temperature-maintaining smart mugs for extended consumption ($80-150)
- Complete professional tea systems with all necessary components ($100-200)
Workplace Integration Strategies
Practical Implementation in Professional Settings
Even the most effective cognitive tea is useless if you can’t practically prepare it in your workplace. This may not be an issue in your home office. These strategies help overcome common office obstacles:
Challenge: Limited Kitchen Access
- Invest in self-contained brewing systems that don’t require trips to the kitchen
- Prepare slightly stronger morning brew and store in an insulated tumbler for a second infusion
- Consider cold brew methods prepared overnight at home
Challenge: Perception of Tea as “Unprofessional”
- Use executive-styled tumblers and modern brewing vessels rather than traditional teaware
- Frame your tea routine in terms of performance optimization rather than wellness
- When asked, have a brief, evidence-based explanation ready that focuses on concrete benefits
Challenge: Time Constraints
- Prepare tea during natural transition moments (computer startup, lunch heating)
- Use rapid-extraction systems that minimize active preparation time
- Consider batch preparation for certain tea types that maintain potency well
Strategic Timing for Optimal Cognitive Support
Your cognitive needs shift throughout the workday, requiring different support at different times:
Early Morning Foundation (7-9am)
- Target State: Activation with stress resilience
- Professional Application: Email processing, day planning, initial task engagement
- Timing Strategy: Prepare at home or immediately upon arrival as part of your workday initiation ritual
Mid-Morning Focus (10am-12pm)
- Target State: Deep concentrated focus
- Professional Application: Complex problem-solving, report writing, detailed analysis
- Timing Strategy: Prepare after completing initial tasks as you transition to deep work
Post-Lunch Revival (1-3pm)
- Target State: Countering post-lunch dip, refreshed alertness
- Professional Application: Preventing afternoon slump, maintaining engagement in meetings
- Timing Strategy: Prepare while eating or immediately after lunch to preempt energy decline
Late Afternoon Sustainer (3-5pm)
- Target State: Sustained mental clarity without evening sleep interference
- Professional Application: Completing important tasks, transition planning for next day
- Timing Strategy: Final tea of workday, prepared as an intentional “finishing strong” ritual

Integration with Productivity Systems
Strategic tea consumption can become a powerful component of productivity methodologies:
Tea-Enhanced Pomodoro Technique
- Use tea preparation as a natural break activity
- Match different tea types to different parts of your work cycle
- Use the brewing process as a mindful transition between work sessions
Deep Work Tea Protocol
- Develop a pre-deep work tea ritual that signals your brain to enter focus mode
- Choose longer-acting teas for sustained work sessions
- Create a post-deep work recovery blend to aid cognitive transition
Meeting Preparation Rituals
- Develop specific tea protocols for different meeting types (presentations, strategy sessions)
- Time consumption for optimal compound activation during the meeting
- Consider portable options for maintaining effects during longer sessions

Building Your Personalized Tea System
Cognitive Task Matching Framework
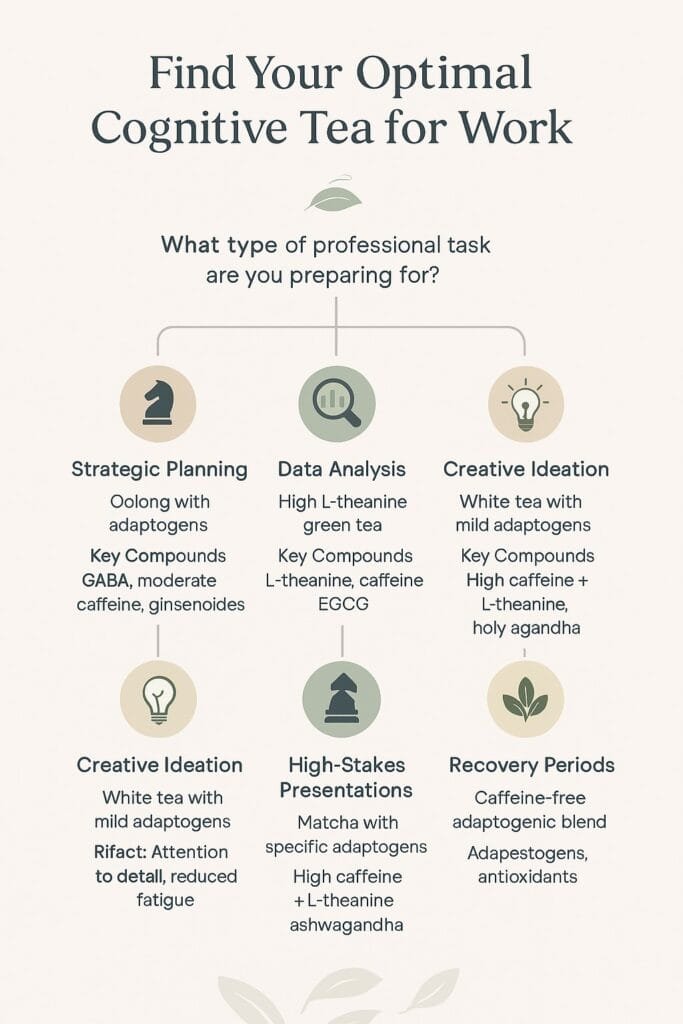
Different professional scenarios benefit from different cognitive enhancement profiles. This framework helps match tea types to specific workplace needs:
| Professional Scenario | Optimal Tea Type | Key Compounds | Desired Effect |
| Strategic planning | Oolong with adaptogens | GABA, moderate caffeine, ginsenosides | Creative connection-making with sustained focus |
| Data analysis | High-L-theanine green tea | L-theanine, moderate caffeine, EGCG | Sustained attention to detail, reduced mental fatigue |
| Creative ideation | White tea with mild adaptogens | Lower caffeine, L-theanine, holy basil compounds | Relaxed alertness promoting novel connections |
| High-stakes presentations | Matcha with specific adaptogens | Higher caffeine, high L-theanine, ashwagandha compounds | Mental clarity with reduced anxiety response |
| Recovery periods | Caffeine-free adaptogenic blends | Adaptogenic compounds, antioxidants | Mental reset and restoration |
Implementation Timeline
Cognitive tea integration is best approached as a systematic implementation rather than an overnight change:
Week 1-2: Baseline Establishment
- Begin with a single morning tea ritual using a basic quality green tea
- Note subjective effects on morning focus and productivity
- Experiment with basic brewing parameters (temperature, steep time)
Week 3-4: Targeted Solution Introduction
- Introduce specific blends matched to your primary cognitive challenges
- Implement proper brewing equipment for your workplace
- Begin tracking cognitive effects more systematically
Month 2: Refinement and Expansion
- Adjust blends based on observed effects
- Expand to strategic mid-day applications
- Fine-tune brewing methods for maximum convenience and effect
Month 3: Full Integration
- Develop complete daily protocol with morning, mid-day and afternoon solutions
- Establish contingency options for high-pressure periods
- Create simplified travel protocol for maintaining benefits while mobile
Realistic Expectations:
- Immediate effects (Days 1-7): Subtle improvements in alertness and focus duration
- Short-term benefits (Weeks 2-4): More noticeable enhancement in specific cognitive areas
- Medium-term advantages (Months 2-3): Established patterns of improved performance
- Long-term gains (Month 4+): Systematic cognitive enhancement integrated into professional identity
Getting Started: Your Action Plan
Based on the comprehensive research in this guide, here are your concrete next steps:
1. Assess Your Primary Cognitive Needs Take a moment to identify your most significant professional cognitive challenges. Is it sustained focus? Creative thinking? Stress resilience? This helps determine your initial tea priorities.
2. Start with Foundational Equipment Begin with just 2-3 essential pieces that work in your specific environment:
- A reliable brewing vessel suitable for your workspace
- A temperature management solution (thermometer or programmable kettle)
- A storage system that maintains tea quality
3. Select Your Starter Protocol Rather than experimenting randomly, start with one of our proven professional protocols:
- Executive Morning Protocol: Morning matcha → mid-day green tea → afternoon adaptogenic blend
- Creative Professional System: Morning white tea with ginkgo → afternoon oolong with holy basil
- Analytical Professional Routine: Morning gyokuro → mid-day rhodiola blend → late afternoon white tea
4. Implement Mindfully
- Start with one tea placement in your day rather than a complete overhaul
- Document effects systematically (a simple spreadsheet or note app works well)
- Adjust brewing parameters before changing tea selections
- Remember that consistency often matters more than perfection

FAQ: Common Questions from Professionals
Conclusion: Strategic Integration for Professional Excellence
Your cognitive tea journey represents a uniquely effective investment in your professional performance—one that enhances mental clarity while providing a valuable moment of mindful pause in an otherwise frantic workday. The research is clear: the right tea, prepared properly and consumed strategically, offers measurable cognitive enhancement that can transform your professional effectiveness.
This guide has provided the framework for making informed decisions about cognitive tea products. In our more specialized posts below, you’ll find detailed reviews of specific products:
- Lifestyle Integration for Cognitive Performance
- Adaptogens & Brain Health
- The Ultimate Guide to Cognitive Teas
Ready to boost your brain health naturally?
Subscribe to our newsletter for updates on new blog posts, news, reviews, and guides.
Join Our Newsletter
Receive updates on new blog posts, news, reviews, and guides
Disclaimer: While cognitive teas offer significant potential benefits, individual responses vary. If you have existing medical conditions or take medications, consult a healthcare provider before incorporating new herbal products, particularly adaptogens.
References
- American Institute of Stress. (2019). Workplace Stress Survey. Retrieved from https://www.stress.org/workplace-stress
- Nobre, A.C., Rao, A., & Owen, G.N. (2008). L-theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 17(S1), 167-168. https://doi.org/10.6133/apjcn.2008.17.s1.40
- Owen, G.N., Parnell, H., De Bruin, E.A., & Rycroft, J.A. (2008). The combined effects of L-theanine and caffeine on cognitive performance and mood. Nutritional Neuroscience, 11(4), 193-198. https://doi.org/10.1179/147683008X301513
- Panossian, A., & Wikman, G. (2010). Effects of adaptogens on the central nervous system and the molecular mechanisms associated with their stress-protective activity. Pharmaceuticals, 3(1), 188-224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010188
- Mancini, E., Beglinger, C., Drewe, J., et al. (2017). Green tea effects on cognition, mood and human brain function: A systematic review. Phytomedicine, 34, 26-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2017.07.008
- Camfield, D.A., Stough, C., Farrimond, J., & Scholey, A.B. (2014). Acute effects of tea constituents L-theanine, caffeine, and epigallocatechin gallate on cognitive function and mood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition Reviews, 72(8), 507-522. https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12120
- Kahathuduwa, C.N., Dassanayake, T.L., Amarakoon, A.M.T., & Weerasinghe, V.S. (2017). Acute effects of theanine, caffeine and theanine-caffeine combination on attention. Nutritional Neuroscience, 20(6), 369-377. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2016.1144845
- Chandrasekhar, K., Kapoor, J., & Anishetty, S. (2012). A prospective, randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy of a high-concentration full-spectrum extract of ashwagandha root in reducing stress and anxiety in adults. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, 34(3), 255-262. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7176.106022
- Dodd, F.L., Kennedy, D.O., Riby, L.M., & Haskell-Ramsay, C.F. (2015). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effects of caffeine and L-theanine both alone and in combination on cerebral blood flow, cognition and mood. Psychopharmacology, 232(14), 2563-2576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3895-0
- Panza, F., Solfrizzi, V., Barulli, M.R., Bonfiglio, C., Guerra, V., Osella, A., Seripa, D., Sabbà, C., Pilotto, A., & Logroscino, G. (2015). Coffee, tea, and caffeine consumption and prevention of late-life cognitive decline and dementia: A systematic review. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 19(3), 313-328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-014-0563-8

